Steel Doors vs. FRP Doors
A Performance Study
Steel Door
FRP Door
Do steel doors or fiberglass reinforced plastic (FRP) doors offer better performance? When comparing steel doors versus FRP doors, steel doors outperform in demanding environments such as fires, tornados, blasts and have superior sound transmission properties. Steel doors are also more cost-effective over the long term due to their durability and low maintenance requirements. However, FRP doors are generally preferred when corrosion resistance or thermal performance are critical.
The quantitative and qualitative data below is based on extensive research including the use of independent testing agencies, standards organizations, and online information, plus interviews door and frame industry professionals.
Performance characteristics were evaluated using quantitative tests such as measurements by a testing organization and/or to defined industry standards. Qualitative evaluation of performance characteristics was primarily through examination of material attributes and interviews with door and frame experts.
Here are our findings.
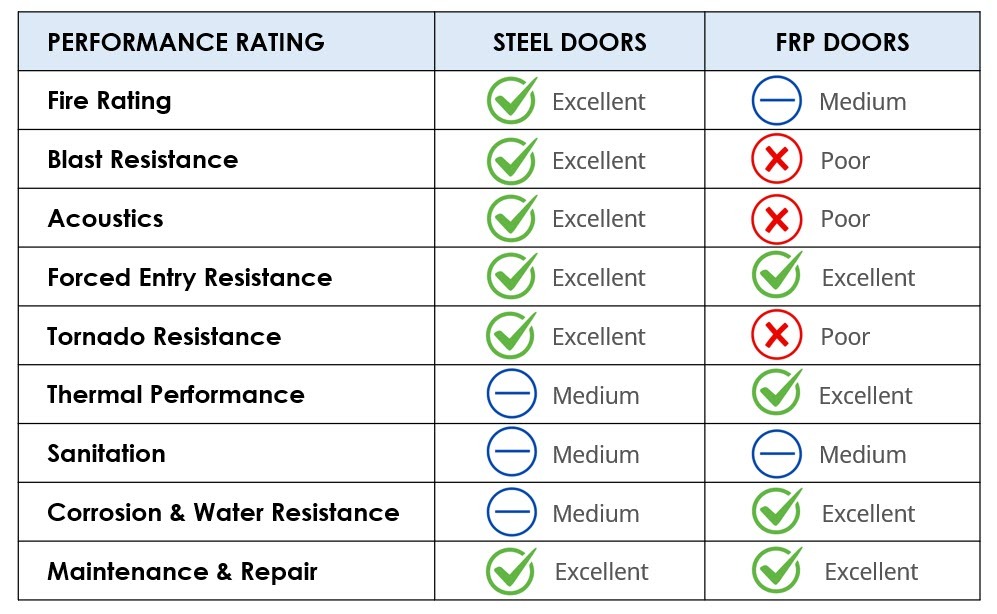
Performance Tables
Fire Rating
Blast Resistance
Sound Transmission/Acoustics
Forced Entry Resistance
Tornado Resistance
Thermal Performance
Relative Performance – Sanitation (Anti-microbial Properties)
Relative Performance – Corrosion and Water Resistance
Relative Performance – Maintenance and Repair
Fire Rating
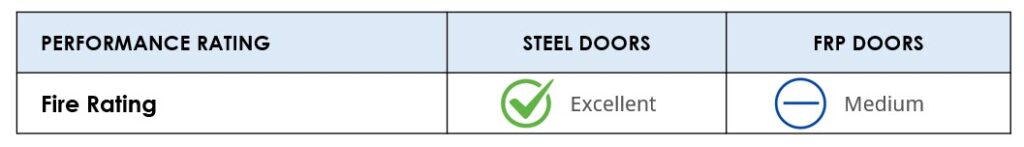
Steel, being a non-combustible material, does not contribute to the spread of fire. Steel is also the only door material that offers a 3-hour fire rating.
FRP doors are not as well-suited to fire resistance as steel due to the natural properties of the material. Fiberglass is only fire-rated a maximum of 90 minutes and requires an intumescent seal.
Relevant Test Methods/Standards:
- NFPA 80 -Standard for Fire Doors and Other Opening Protectives
- UL 10C – Standard for Positive Pressure Fire Tests of Door Assemblies
CONCLUSION
Steel doors are the sole door material to deliver a 3-hour fire rating and have the best fire rating capabilities. They are also generally priced lower than fiberglass fire-rated doors.
Blast Resistance
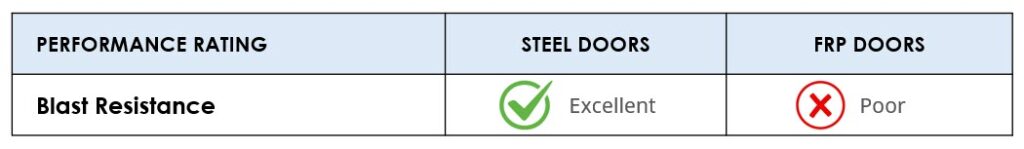
Blast resistant steel door assemblies can pass the common standards for blast resistant openings. Steel doors that are blast resistant are also available in fire or windstorm rated, bullet resistant, and with vision lights.
Fiberglass doors are generally not rated as blast resistant.
Relevant Test Methods/Standards:
- ASTM F2247 – Standard Test Method for Metal Doors Used in Blast Resistant Applications
- ASTM F2927 – Standard Test Method for Door Systems Subject to Airblast Loadings
- ASTM F1642 – Standard Test Method for Glazing and Glazing Systems Subject to Airblast Loadings
CONCLUSION
Blast resistant steel door assemblies pass the common standards for blast resistant openings, whereas FRP doors fail these tests.
Sound Transmission/Acoustics
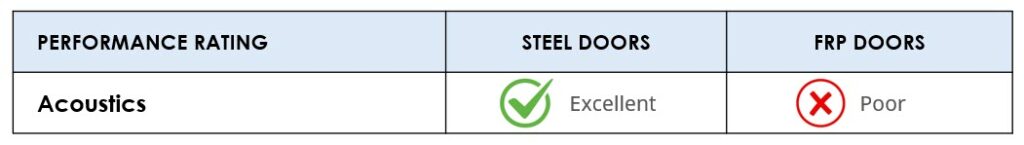
Steel offers the highest STC rating of any door material. Single steel acoustic door ratings generally range from STC 32-55 (and up to 66 with highly specialized doors). Steel acoustic doors can achieve a 3-hour fire rating. Vision lights and embossments are available too.
Fiberglass doors have acoustic ratings that generally range from STC 29-39; however, they are rarely used in sound reduction environments due to their lower STC ratings.
Relevant Test Methods/Standards:
- ASTM E90 – Standard Test Method for Laboratory Measurement of Airborne Sound Transmission Loss of Building Partitions and Elements
- ASTM E413 – Classification for Rating Sound Insulation
- ASTM E336 – Standard Test Method for Measurement of Airborne Sound Attenuation between Rooms in Buildings
CONCLUSION
Steel doors have the best STC performance characteristics. They are well suited to sound reduction specifications and offer lower lifecycle costs than FRP doors.
Forced Entry Resistance
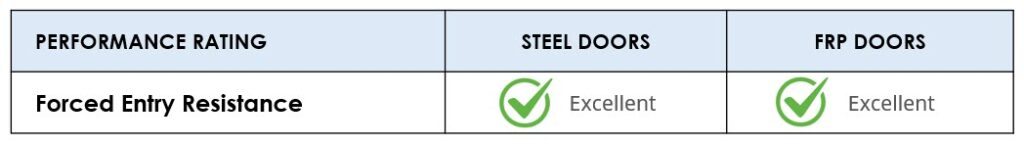
Steel door assemblies pass the three commonly specified test criteria for forced entry resistance in government and non-government buildings.
FRP doors are strong and able to meet forced entry standards; however, they are generally more expensive.
Relevant Test Methods/Standards:
- ASTM F1233 – Standard Test Method for Security Glazing Materials and Systems,
- ASTM F3038 – Standard Test Method for Timed Evaluation of Forced-Entry-Resistant Systems
- SD-STD-01.01 – Forced Entry and Ballistic Resistance of Structural Systems
CONCLUSION
Due to its inherent strength and lower lifecycle costs, steel is the optimal and most commonly specified door material for forced entry resistant openings.
Tornado Resistance
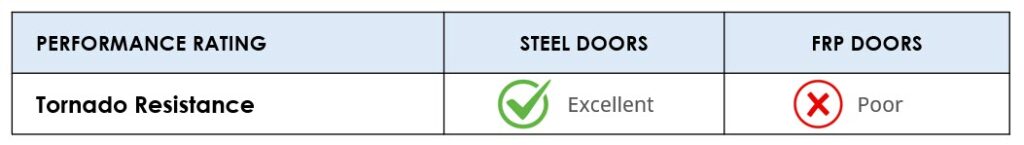
Steel doors pass the tornado resistance tests of the two primary standards developers, FEMA and ICC. This includes testing doors at wind speeds up to 250 mph.
FRP doors are not listed for tornado resistance since they fail to meet the relevant standards.
Relevant Test Methods/Standards:
- FEMA 361 – Safe Rooms for Tornadoes and Hurricanes
- ICC 500 – Standard for the Design and Construction of Storm Shelters
CONCLUSION
Steel is the only door material that is viable for tornado resistant opening applications.
Thermal Performance
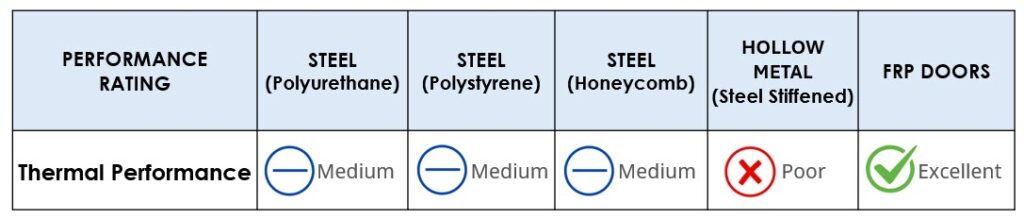
Steel doors with a polyurethane core transmit little heat compared to other materials and have a U-Factor of .38 which is just above fiberglass. Steel doors with polystyrene or honeycomb cores also transmit little heat compared to other materials. Hollow metal doors with a steel stiffened core transfer the most heat of the steel core materials with a U-Factor of .61.
FRP doors have superior thermal performance with a typical U-Factor of .23 and an R-Value of 2.85.
Relevant Test Methods/Standards:
- ASTM C1199 – Standard Test Method for Measuring the Steady-State Thermal Transmittance of Fenestration Systems Using Hot Box Methods
- ASTM C1363 – Standard Test Method for Thermal Performance of Building Materials and Envelope Assemblies by Means of a Hot Box Apparatus
- ASTM E1423 – Standard Practice for Determining Steady State Thermal Transmittance of Fenestration Systems
CONCLUSION
Steel doors with a polyurethane core transmit little heat and have a U-Factor that is just above fiberglass. Fiberglass doors have the best natural thermal performance compared to steel.
Relative Performance – Sanitation (Anti-microbial Properties)
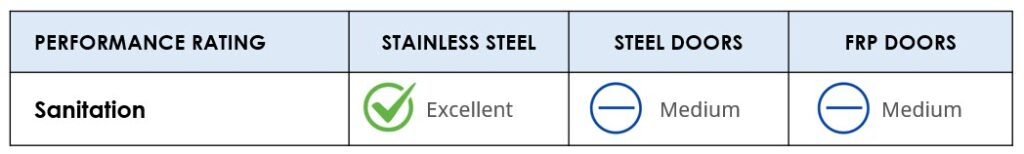
Stainless steel doors with a custom seamless edge have superior anti-microbial properties. They wash easily and sanitize thoroughly, making them a good choice for sanitary environments, such as food handling and medical.
Steel is well suited to environments requiring high levels of sanitation. It washes easily when specified with the appropriate finish and a custom seamless edge. Antimicrobial resin is available for additional protection.
Fiberglass doors are also selected for their antimicrobial properties for use in environments requiring high sanitation.
CONCLUSION
Other than all glass doors, stainless steel and steel doors have the best sanitation properties versus FRP doors.
Relative Performance – Corrosion & Water Resistance
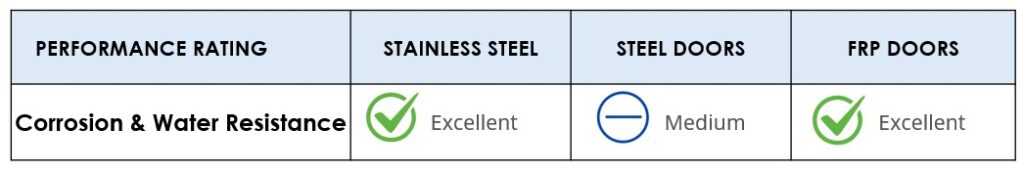
Stainless steel doors are commonly specified for environments requiring corrosion or water resistance. Type 316 is required for high salt or high chemical environments, such as coastal applications (salt) and indoor swimming pools.
Steel earned a medium performance rating for corrosion and water resistance. While naturally susceptible to rust, there are cost-effective galvanized coatings and applied finishes are readily available to prevent corrosion in steel doors.
Fiberglass is naturally corrosion resistant, and FRP doors are often selected for use in corrosive environments.
CONCLUSION
Stainless steel and fiberglass doors have excellent performance in relation to corrosion resistance.
Relative Performance – Maintenance & Repair
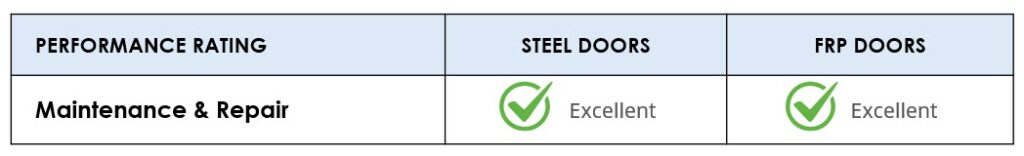
Steel doors do not crack or dent easily and can often be repaired in the field with body filler or re-welding for a relatively low cost.
FRP doors also offer superior performance for maintenance and repair. However, the purchase price of a fiberglass door is cost prohibitive for many projects.
CONCLUSION
Steel doors offer the best price/performance advantage for maintenance and repair.


