Industry Alerts (A-K Series)
SDI 127 A-K
View PDF
Table of Contents
127-D Electric Hardware Preparation for Frames in Stud Walls
127-F Butted Frames Rough Opening Sizes
127-G Environmental Considerations Relating to Factory Painted Steel Doors and Frames
127-I Grouting Frames in Drywall
127-K Improper Wedges as Hold-Opens
WITHDRAWN: 127-L Buyer Beware: Steel Doors with Lead-Based Primer
SDI 127A-24
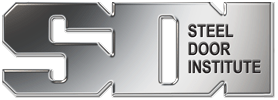
End Channel Location
This alert is intended to raise awareness of the potential of interferences between top or bottom channels and the installation of surface mounted hardware items such as closers or door bottom seals.
The steel door industry utilizes a variety of end channel designs in standard doors. The most common are flush type end channels or inverted end channels. The inverted (legs upward) end channels in many cases may create a necessity to reposition the mounting holes for hardware items such as
regular arm closers, surface overhead stops/holders, or door bottom accessories. To avoid interference with the “web” of the end channel, mounting screws must be slightly repositioned.
Illustrated below are example channel conditions on standard steel doors. End channel systems vary by manufacturer.
It is suggested that the hardware manufacturer and/or a hardware consultant be contacted for resolution of a hardware installation conflict.
SDI 127B-23
Door Edge Cutouts
This alert is intended to raise awareness of the minimum distances required for common hardware preparations from bend lines on the edges of steel doors.
The ability to form a crisp aesthetic cutout in the edge of a steel door, especially in the vicinity of a bend line is directly influenced by the steel thickness and the proximity of the cutout to the bend line. A cutout too close to the bend line will result in a flare-out of the cutout area due to unevenly distributed stress along the brake die or rollform rollers.
The following illustrations are intended to convey dimensional limitations of the hardware items to be mortised into the edge of 1 3/4″ thick standard steel doors.
Certain lock fronts, concealed hinges, strikes, or electrical devices do not comply with these limitations. The resulting potential for inaccuracy or lack of aesthetics is inherent in the manufacturing processes and is not to be considered a defect.
Notes:
- Tolerances – All values which do not carry specific tolerances or are not marked maximum or minimum shall have the following tolerances: Linear dimensions shall be ± 1/16 in. Weight or force shall be ± 2%. Angles shall be ± 2 degrees. Where only minus tolerances are given, the dimensions are permitted to be exceeded at the option of the manufacturers.
- Gauge vs. Thickness – While the term ‘gauge’ is no longer common for defining material thickness it is still used to specify doors and frames for ordering purposes. The term ‘thickness’ is used when defining the actual dimension of an item, and the term ‘gauge’ is used in the context of specifying a particular door or frame.

SDI 127C-23
Frame Cutout Limits
This alert is intended to raise awareness of the minimum distances required for common hardware preparations from bend lines on steel frames.
The ability to form a crisp aesthetic cutout in steel frames, especially in the vicinity of a bend line is directly influenced by the steel thickness and the proximity of the cutout to the bend line. A cutout too close to the bend line will result in a flare-out of the cutout area due to unevenly distributed stress along the brake die or rollform rollers.
The following illustration is intended to convey dimensional limitations of the hardware items to be mortised into the face, rabbet or stop of steel frames. Certain concealed hinges, strikes, or electrical devices do not comply with these limitations. The resulting potential for inaccuracy or lack of aesthetics is inherent in the manufacturing processes and is not to be considered a defect.
Notes:
- Tolerances – All values which do not carry specific tolerances or are not marked maximum or minimum shall have the following tolerances: Linear dimensions shall be ± 1/16 in. Weight or force shall be ± 2%. Angles shall be ± 2 degrees. Where only minus tolerances are given, the dimensions are permitted to be exceeded at the option of the manufacturers.
- Gauge vs. Thickness – While the term ‘gauge’ is no longer common for defining material thickness it is still used to specify doors and frames for ordering purposes. The term ‘thickness’ is used when defining the actual dimension of an item, and the term ‘gauge’ is used in the context of specifying a particular door or frame.

SDI 127D-24
Electric Hardware Preparation for Frames in Stud Walls
Steel or wood stud drywall constructions methods and frame anchorage could result in interference between the stud and the electric strike, hinge or other electrical hardware preparation. Notching the stud could result in compromising the stability of the frame and invalidating the fire rating of the opening.
Dependent on the dimensions of the strike, the cutouts may extend beyond the frame face or the returns, thus leaving critical strike parts or wiring exposed.
Consideration should be given to specifying a strike suitably sized to fit the confines of a standard 2″ face frame or specify an alternate frame profile with larger frame faces that will accommodate it.
Situations exist where the electrical hardware preparation does not allow the drywall to penetrate the throat of a fire rated frame the required 1/2-inch in the immediate area of the hardware. When this occurs, a penetration or joint seal (e.g. intumescent caulk) listed for gypsum wall assemblies must be applied to the affected area; thereby, sealing any potential gap and ensuring the continuity of the fire barrier.
SDI 127E-23
Prime Painted Materials
Prime Painted Doors, Frames, and Accessories (where applicable) shall comply with the acceptance criteria specified in ANSI/SDI A250.10. Doors and frames are cleaned and treated prior to painting to ensure maximum paint adhesion. All exposed surfaces are then given a factory-applied coat of rust inhibiting “direct to metal” type primer. The primer is then baked, air dried, or otherwise cured as appropriate for the primer.
This process is intended to protect the steel surfaces for a period of time under reasonable weather exposure conditions. Factory applied primer coatings may be somewhat porous in order to accept finish coatings. The primer coating may therefore be susceptible to the action of moisture or ambient moisture condensation during shipping or storage. For example, transportation of materials in unprotected “open” trucks during inclement weather (rain or snow) or on roadways where salt or other snow melting agents are used will deteriorate the primer. Extended exposure to such conditions may result in rusted or water stained areas. ANSI/SDI A250.8 (SDI-100) paragraph 4.1 presents Industry recommended jobsite storage requirements.
Should the primer become scratched, abraded, rusted or stained, the affected areas may rust unless sanded and reprimed with a suitable “direct to metal” primer containing rust inhibitors.
Prior to application of finish coats, the substrate shall be inspected by the Painting Contractor. All Architectural Specification requirements along with all requirements of the paint manufacturer shall be followed. These will generally include scuff sanding of the substrate to remove foreign materials, scratches or abrasions from construction processes, along with any special or mandatory requirements for primer touch-up or additional primers required by the paint system.
MOST IMPORTANTLY, the field applied primer and finish paint “systems” must be designed for direct to metal applications and contain rust inhibiting properties.
IF COATING COMPATIBILITY IS A CONCERN, contact the SDI Manufacturers or their local distributors who can provide information or “sample” materials for the painting contractor’s use.
SDI 127F-23
Butted Frames Rough Opening Sizes
The variety of existing wall anchors available from SDI Members allow Standard Steel Door Frames to be a reliable option for existing wall, structural steel wall framing or retrofit installations utilizing a butted to wall application. In order to make the installation successful, careful consideration shall be given to all tolerances involved and that sufficient clearance is figured to allow for them.
It has been “customary” to allow clearance around the frame perimeter when establishing rough opening sizes or when figuring non-standard overall frame sizes. This clearance is necessary to compensate for any allowable manufacturing tolerances, installation tolerances, or substrate conditions. Tolerances and clearances are referenced both pictorially and verbally in a number of Industry documents such as:
- SDI-110 Standard Steel Doors & Frames for Modular Masonry Construction (butted frames)
- SDI-111 Recommended Details for Standard Steel Doors, Frames, Accessories and Related Components (existing wall anchors)
- SDI-117 Manufacturing Tolerances for Standard Steel Doors and Frames (manufacturing tolerances)
- ANSI/SDI A250.8 Specifications for Standard Steel Doors and Frames (SDI-100)
- ANSI/SDI A250.11 Recommended Erection Instructions for Steel Frames
- NAAMM HMMA 840 Guide Specification for Receipt, Storage and Installation of Hollow Metal Doors and Frames
- NAAMM HMMA 841 Tolerances and Clearances for Commercial Hollow Metal Doors and Frames
Frames will “fit and function” if made to these dimensional tolerances and installed within tolerances. There is, however, relatively no assurance that the substrate (walls) will be of suitable size or alignment.
We therefore recommend that the rough openings for these cases be no less than 3/16″ larger on all 3 sides than the “intended” overall frame size. (Example: 3070 standard frame = 3′-4 3/8″ x 7′-2 3/16″). The installer carries the responsibility for shimming and aligning as necessary. Gaps are normally sealed as part of the installation or caulking/painting process. Architectural Specifications are to be consulted to determine the appropriate sealant material to be used at fire door or smoke control frames.
Note:
- All values which do not carry specific tolerances or are not marked maximum or minimum shall have the following tolerances: Linear dimensions shall be ± 1/16 in. Weight or force shall be ± 2%. Angles shall be ± 2 degrees. Where only minus tolerances are given, the dimensions are permitted to be exceeded at the option of the manufacturers.
SDI 127G-23
Environmental Considerations Relating to Factory Painted Steel Doors and Frames
There is an industry need for a comprehensive revision of specifications, practices and procedures that will allow compliance with existing and future regulations. The member companies of the Steel Door Institute have taken the steps needed to eliminate from their primers, those elements identified by regulatory authorities as hazardous to human health and the environment. This is not only a moral responsibility toward society, but also a survival responsibility toward the business. The SDI encourages specification writers to look at these issues very carefully when they specify coating requirements.
Federal and state laws have regulated the management of hazardous waste so as to not pose a threat to the environment or human health. Environmental protection agencies are very strict in regulations that affect coating applications, by limiting the emission to the atmosphere of the amount of VOC (Volatile Organic Compound), which has curtailed the use of solvent base paints.
Section 313 of the Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (Title III) sets up the reporting requirements in the metal fabricating industry for all wastes containing any listed toxic chemical, which affects the use of heavy metals (such as Zinc-Chromates) as rust inhibitors.
SDI 127H-23
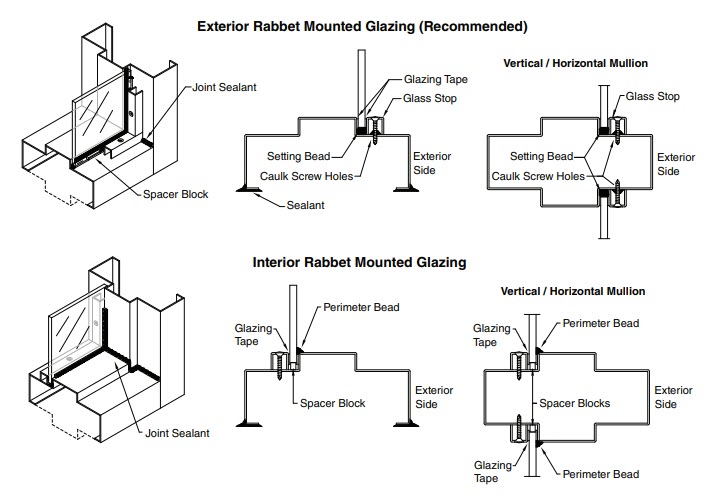
Water Penetration
Borrowed light assemblies, transom, sidelight, and combination transom sidelight frames are not factory sealed to prevent water penetration. In situations where water penetration is a concern, the contractor must seal all joints that are exposed to the elements after the frame assembly is installed.
Whenever possible, it is strongly recommended that glass and glazing be installed on the exterior rabbet of the frame assembly. This will help act as a deterrent to water penetration.
The member companies of the hollow metal industry can not control the workmanship associated with the frame installation; therefore, it is the responsibility of the installer to assure all steps are taken to prevent water penetration.
SDI 127I-23
Grouting Frames in Drywall
Some architectural specifications require frames in stud and drywall partitions to be filled with grout for sound deadening or to enhance structural integrity.
The Steel Door Institute is opposed to this practice for the following reasons:
- In drywall construction, this moisture has two places to go. It can soak into the drywall, potentially destroying its cohesive integrity and thus the ability to retain anchors or frame integrity, or it can leach downward where it will cause premature rusting of anchors, screws, stud connections, bottom of frames, etc.
- Grouting does not appreciably afford any additional structural rigidity to the frame. As an example, slip-on drywall frames have passed fire and hose stream tests, cycle tests, and in some cases impact tests without being grouted.
- If the intention is for sound deadening, SDI-128 Guidelines for Acoustical Performance of Standard Steel Doors and Frames (Section 3) should be consulted. In addition, the same insulation as used between wall studs (generally lightly packed fiberglass) will serve as a sound deadener without the potential for damage to the frame or wallboard.
Higher STC (Sound Transmission Class) products (over STC 40) may require that the frame be grouted with a cement-based grout or mortar as this was the tested condition. In these cases, the frames should be grouted and thoroughly cured prior to installation of the frame in the drywall wall.
It is therefore the opinion of the Steel Door Institute that grouting should not be specified or used for drywall construction except as described above.
Read more about the Risks of Grouting Frames.
SDI 127J-23
Back Coating of Frames
Some Architectural Specifications require steel frames to be back coated with a “bituminous” coating for corrosion protection and sound control. The term “Bituminous” is defined as an asphalt or tar material obtained as a residue from heat refined petroleum. For years it was not recommended by Steel Door Institute for frames to be factory back coated. This procedure was to be done at the jobsite by the contractor or appropriate trade immediately prior to installation of the frame.
Modern materials available today offer manufacturers the opportunity to back coat frames with a more user friendly and environmentally sound product. Some of these coatings are free of VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds) and can also easily be used to touch up frames that are welded on-site.
For corrosion protection, ANSI/SDI A250.11 paragraph 2.2.1 clearly states that “the contractor responsible for installation” applies corrosion resistant coatings only where specified for anti-freeze agents in the mortar. “Anti-freeze agents are accelerators (e.g. – calcium chloride) intended to increase the rate of mortar strength development not reduce the freezing point of mortar. The Steel Door Institute recommends not using any accelerating additives to the mortar used to back-fill or grout frames. ANSI/SDI A250.11 paragraph 2.3.2 states that “grout shall be mixed to provide a 4″ maximum slump”. Grout mixed to a thinner consistency has excessive moisture and requires longer cure times which increase the potential for corrosion.
SDI 127K-23
Improper Wedges as Hold-Opens
It has come to the attention of the Steel Door Institute (SDI) that cleaning or maintenance personnel have been incorrectly wedging doors to hold them open. This has been reported mainly in health care or hotel-motel installations at patient rooms, utility rooms, sleeping rooms, and even stairways.
Instead of using rubber wedges at the bottom of doors or suitable hold-open mechanisms, wedges of various materials have been inserted between the hinge edge of the door and the hinge jamb. This practice puts an abnormal stress on the hinge reinforcements, hinge knuckles, and attachment screws causing potential damage to any or all of these components.
Damage, loosening, or failure resulting from this practice shall not be construed as a door, frame, or hardware defect or warranty issue. The SDI strongly discourages the use of wedges in this manner or any methods for holding doors open that will compromise the fire or life safety integrity of the openings.
The importance of unrestricted closing and latching of door openings in fire situations is further discussed in Sections 9 through 9.5 of SDI-118 Basic Fire Door Requirements.